April 9, 2024 Notes gathered by Bill Dawson
Nebulized hydrogen peroxide is an effective treatment for colds, flu, Covid, and other respiratory infections. This is an old therapy that is still quite effective and has the advantage that pathogens don’t become resistant to it. The hydrogen peroxide sold in drug stores has proprietary stabilizing chemicals added to it. While that could be used in a pinch, it is best to purchase food grade hydrogen peroxide for use in a nebulizer, diluted with a saline solution as described below.
“Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) consists of a water molecule (H2O) with an extra oxygen atom (O2), and it is the additional oxygen atom that allows it to inactivate viral pathogens. Some of your immune cells produce hydrogen peroxide to destroy pathogens. By killing the infected cell, viral reproduction is stopped. So, hydrogen peroxide therapy aids your immune cells to perform their natural function more effectively.
Many studies have investigated the use of hydrogen peroxide against different pathogens. For example, a 2020 review40 of 22 studies found that 0.5% hydrogen peroxide effectively inactivated a range of human coronaviruses, including those responsible for SARS and MERS, within one minute of exposure.
According to Brownstein, all pathogens studied to date have been found to succumb to hydrogen peroxide, albeit at varying concentrations and for different amounts of exposure.
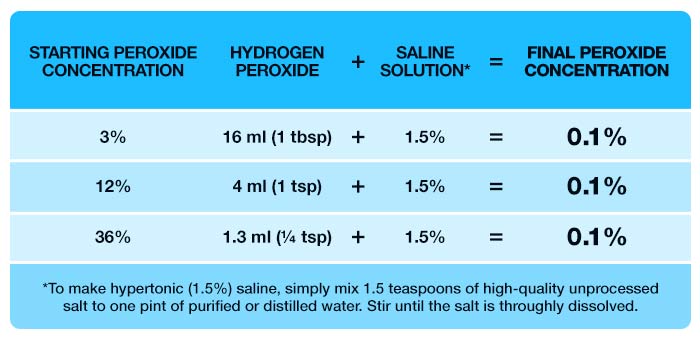
While you can use virtually any percentage of food grade peroxide, it’s crucial to dilute it properly before use. What you want is a 0.1% dilution, so even a 3% hydrogen peroxide will need to be diluted at least 30 times.
In a pinch, you could use commercial 3% hydrogen peroxide, the stuff used for wound care, but I don’t recommend routine use of it as it contains stabilizing chemicals that can detract from the benefits. Also, you want to dilute the hydrogen peroxide with hypertonic saline, not plain water, as the lack of electrolytes in the water can damage your lungs if you nebulize that. Using saline prevents the osmotic differential that can damage lung cells.
To end up with a final peroxide/hypertonic saline solution concentration of 0.1%, you need to go through two steps:
- Create the hypertonic saline solution
- Dilute the peroxide
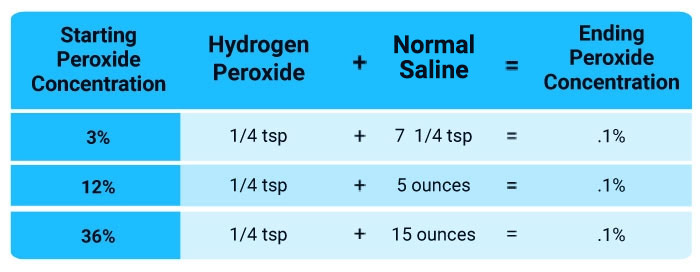
I used to recommend using normal saline, which contains 0.9% salt, but a 2021 study41 found that a 1.5% sodium chloride solution (hypertonic saline) achieved a 100% inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 replication in vitro (in cell culture). Using lower levels of saline, like 1.1%, only inhibited 88%. So, I now recommend using hypertonic saline instead, which would be slightly less than double the amount of salt used to make normal saline.
To make hypertonic (1.5%) saline, simply mix 1.5 teaspoons of high-quality unprocessed salt to one pint of purified or distilled water. Stir until the salt is thoroughly dissolved. Be sure to use proper measuring spoons and not a regular kitchen teaspoon. For even greater precision, you could use a digital scale to measure out exactly 7.1 grams of salt.
If the 1.5% hypertonic solution causes nasal burning, irritation or cough, you can lower the concentration to 0.9% salt, which is isotonic normal saline. For this you would decrease the salt to one level teaspoon to one pint of water. Once you have your saline solution and a food grade hydrogen peroxide, dilute the peroxide according to the following chart, based on the concentration you’re starting with.
[Dr. Brownstein prefers to use a 0.04% concentration which he achieves by diluting 3ml of a 3% mixture, adding it to 250ml of normal saline. To this, he adds one drop of Lugol’s solution prior to nebulizing.]
!WARNING:
Food grade peroxide at concentrations of 12% and 36% should NEVER be used full-strength either topically or internally. It MUST be diluted or severe injury can occur. Your safest bet is to use 3% food grade peroxide and dilute it as indicated so you end up with a solution of 0.1%.
Once you have your peroxide-saline solution, simply pour 1 teaspoon of it into the nebulizer and inhale the entire amount. If you like, you can add one drop of 5% Lugol’s iodine solution to the nebulizer as well. Some find it boosts the effects.
I recommend using nebulized peroxide for any suspected respiratory infection, and the earlier you start, the better. If you’re already presenting with a runny nose or sore throat, use the nebulizer for 10 to 15 minutes four times a day until your symptoms are relieved.
You can also use nebulized hydrogen peroxide for prevention and maintenance, which may be advisable during flu season. There is no danger in doing it every day if you’re frequently exposed, and there may even be additional beneficial effects, such as a rapid rise in your blood oxygen level.”
Source Scientists Warn Bird Flu Outbreak Could Be 100 Times Worse Than COVID
From another Mercola article: nebulizer recommendation and more dilution instructions, showing how to make a 0,04%concentration.
“Nebulized hydrogen peroxide is extremely safe. Brownstein has used it for 25 years with no ill effects being found. It’s also incredibly inexpensive, and you can administer it at home, without a prescription. In my view, it is one of the absolute best therapies for viral infections like SARS-CoV-2 or even worse respiratory viruses that will likely be unleashed in the future.
You need to buy a desktop nebulizer (it needs to produce a very fine mist and desktop versions are stronger than handheld battery operated models). The one I use is the Pari Trek S Compressor Aerosol System. The large battery option is unnecessary as you can simply plug in the device to run it when you need it.
Please understand, though, that the Pari Trek S is designed to treat asthmatics and as such only comes with a mouthpiece. While this would get the peroxide in the lungs where it is needed, it does nothing to reach the sinuses, which are also likely infected. This is why it would be worth pick up some face masks on Amazon to use instead of the mouthpiece as they are only about $10.
It is important to acquire this BEFORE you need it, as the sooner you treat the infection the better your results will be, although the testimonials are unbelievably impressive even in late stage illness. It is not necessary to treat yourself preventively, but only if you are sick or exposed to someone who is.
While I’ve been using a 0.1% dilution, Brownstein uses an even lower concentration of just 0.04%. Neither Brownstein nor I recommend using commercial 3% hydrogen peroxide found in most grocery stores, however, as it has potentially toxic chemical stabilizers in it. Then take 3 to 5 ml and put that into the nebulizer and inhale the entire amount.
You can do this every hour when you are sick until you start to notice improvement and then back down to every four to six hours and continue until you are over the illness.
Since you are not using full strength 3% peroxide and diluting it by 30 to 50 times, it is unlikely the stabilizers will present a problem, but to be safe it is best to use FOOD-GRADE peroxide. Also remember not to dilute it with plain water as the lack of electrolytes in the water can damage your lungs if you nebulize that. You will need to use saline or add a small amount of salt to the water to eliminate this risk.
Brownstein also dilutes the peroxide with sterile water and saline rather than distilled water. Using saline prevents the osmotic differential that can cause damage to lung cells. Brownstein dilutes the 35% food-grade peroxide as follows. When nebulizing, Brownstein also adds one drop of 5% Lugol’s solution to the nebulizer as well.
- Dilute 35% food-grade peroxide down to 3% by mixing 1 part peroxide with 10 parts sterile water
- Take 3 cubic centimeters (CCs) of that 3% dilution and add it to a 250CC bag of normal saline. This brings it down to a .04% hydrogen peroxide concentration”
Source: How Nebulized Peroxide Helps Against Respiratory Infections
More on how hydrogen peroxide therapy works.
“Your immune cells actually produce hydrogen peroxide. This is in part how your immune system kills cells that have been infected with a virus. By killing the infected cell, viral reproduction is stopped. So, hydrogen peroxide therapy is in essence only aiding your immune cells to perform their natural function more effectively.
Hydrogen peroxide is also a key redox signaling agent. As explained in the March 30, 2020, review article from my absolute favorite journal Nature Reviews Molecular Biology “Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) as Pleiotropic Physical Signaling Agents”:7
“At the low physiological levels in the nanomolar range, H2O2 is the major agent signaling through specific protein targets, which engage in metabolic regulation and stress responses to support cellular adaptation to a changing environment and stress …
Recent methodological advances permit the assessment of molecular interactions of specific ROS [reactive oxygen species] molecules with specific targets in redox signaling pathways.
Accordingly, major advances have occurred in understanding the role of these oxidants in physiology and disease, including the nervous, cardiovascular and immune systems, skeletal muscle and metabolic regulation as well as ageing and cancer.
In the past, unspecific elimination of ROS by use of low molecular mass antioxidant compounds was not successful in counteracting disease initiation and progression in clinical trials. However, controlling specific ROS-mediated signaling pathways by selective targeting offers a perspective for a future of more refined redox medicine.”
In short, hydrogen peroxide is a major ROS, but while ROS are typically thought of as “all bad,” this is a gross oversimplification. As noted in this paper, blanket elimination of ROS is inadvisable as they actually serve important signaling functions. The paper, which is behind a paywall, further explains:8
“Steady-state physiological flux of H2O2 to specific protein targets leads to reversible oxidation, thereby altering protein activity, localization and interactions, which contributes to orchestration of various processes in cells and organs, including cell proliferation, differentiation, migration and angiogenesis. This state of low-level H2O2 maintenance and its associated physiological redox signaling is called ‘oxidative eustress.'”
Contrary to oxidative stress or oxidative distress, oxidative eustress denotes an oxidative challenge that has positive or beneficial effects and is essential in redox signaling.”
From Could Hydrogen Peroxide Treat Coronavirus?
Hydrogen peroxide functions as a signaling molecule in various biological pathways as described in this abstract:
“Increasing evidence implicates hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) as an intra- and intercellular signaling molecule that can influence processes from embryonic development to cell death. Most research has focused on relatively slow signaling, on the order of minutes to days, via second messenger cascades. However, H2O2 can also mediate subsecond signaling via ion channel activation. This rapid signaling has been examined most thoroughly in the nigrostriatal dopamine (DA) pathway, which plays a key role in facilitating movement mediated by the basal ganglia. In DA neurons of the substantia nigra, endogenously generated H2O2 activates ATP-sensitive K+ (KATP) channels that inhibit DA neuron firing. In the striatum, H2O2 generated downstream from glutamatergic AMPA receptor activation in medium spiny neurons acts as a diffusible messenger that inhibits axonal DA release, also via KATP channels. The source of dynamically generated H2O2 is mitochondrial respiration; thus, H2O2 provides a novel link between activity and metabolism via KATP channels. Additional targets of H2O2 include transient receptor potential (TRP) channels. In contrast to the inhibitory effect of H2O2 acting via KATP channels, TRP channel activation is excitatory. This review describes emerging roles of H2O2 as a signaling agent in the nigrostriatal pathway and other basal ganglia neurons.”
Source: H2O2: A Dynamic Neuromodulator
“Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is widely regarded as a cytotoxic agent whose levels must be minimized by the action of antioxidant defence enzymes. In fact, H2O2 is poorly reactive in the absence of transition metal ions. Exposure of certain human tissues to H2O2 may be greater than is commonly supposed: substantial amounts of H2O2 can be present in beverages commonly drunk (especially instant coffee), in freshly voided human urine, and in exhaled air. Levels of H2O2 in the human body may be controlled not only by catabolism but also by excretion, and H2O2 could play a role in the regulation of renal function and as an antibacterial agent in the urine. Urinary H2O2 levels are influenced by diet, but under certain conditions might be a valuable biomarker of ‘oxidative stress’.”
